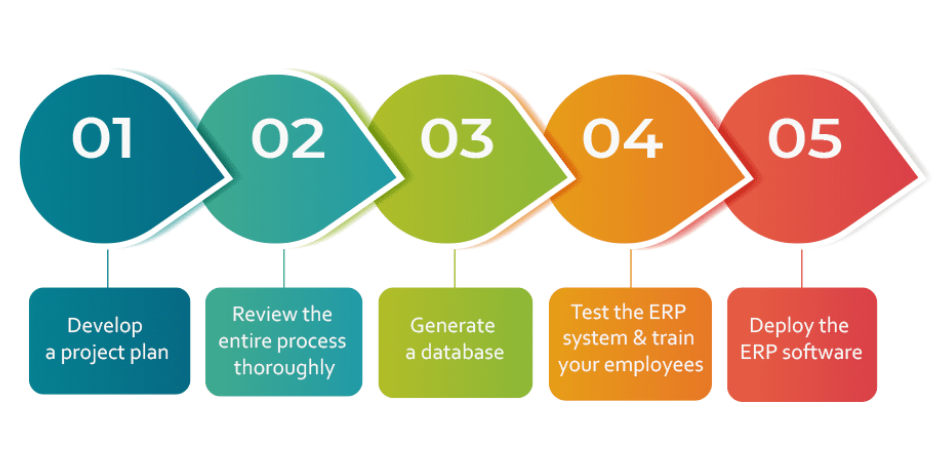

Enterprise Resource Planning
The Information Technology industry is renowned for its adoption of acronyms, which are often widely used, but not fully understood. The term ‘ERP’ itself is not self explanatory and refers to the business software that has been designed to record and manage your enterprise data. An ERP System automates and integrates core business processes such as taking customer orders, scheduling operations, and keeping inventory records and financial data.
At its core, an ERP is an application that automates business processes, and provides insights and internal controls, drawing on a central database that collects inputs from departments including accounting, manufacturing, supply chain management, sales, marketing and human resources (HR).
Once information is compiled in that central database, leaders gain cross-departmental visibility that empowers them to analyze various scenarios, discover process improvements and generate major efficiency gains. That translates to cost savings and better productivity as people spend less time digging for needed data.
ERP software that’s tailored to meet the needs of an individual business pays major dividends, making these systems a critical tool for companies across industries
and of all sizes. Many of the world’s best-known and most successful firms have leaned on ERP for the last quarter century. Now, this software can be configured and priced to meet the needs of all-size businesses. Put simply, an ERP system helps unify people, core business processes and technology across an organization.
Why Is ERP Important for Businesses?
ERP systems have become table stakes for businesses looking to use resources wisely. They can help leaders reallocate human and financial capital or build more efficient core business processes that save money without sacrificing on quality or performance.
ERP systems can drive huge improvements in the effectiveness of any organization by:
- Assisting you in defining your business processes and ensuring they are complied with throughout the supply chain
- Protecting your critical business data through well-defined roles and security access
- Enabling you to plan your work load based on existing orders and forecasts
- Providing you with the tools to give a high level of service to your customers
- Translating your data into decision making information
Benefits of Our ERP for your Business
Integration across all business processes – To realize the full benefits of an ERP system it should be fully integrated into all aspects of your business from the customer facing front end, through planning and scheduling, to the production and distribution of the products you make.
Automation enhances productivity – By automating aspects of business processes, ERP makes them more efficient, less prone to error, and faster. It also frees up people from mundane tasks such as balancing data.
Increase overall performance – By integrating disparate business processes, ERP ensures coherence and avoids duplication, discontinuity, and people working at cross purposes, in different parts of the organization. The cumulative positive effect when business processes integrate well is overall superior performance by the organization.
Quality Reports and Performance Analysis – Analysis on ERP will enable you to produce financial and boardroom quality reports, as well as to conduct analysis on the performance of your organization.
Integrates across the entire supply chain – A best of breed ERP system should extend beyond your organization and integrate with both your supplier and customer systems to ensure full visibility and efficiency across your supply chain.
Most ERP software is built around established best practices. The software provider designs workflows and functionality based on its experience working with hundreds or thousands of customers and encourages as much conformity as possible, though there is often flexibility to adjust processes.
Adhering to industry-standard best practices has major business advantages. Companies often find that they improve and modernize their processes, and in turn maximize operational efficiency and avoid falling behind competitors. Observing best practices also helps companies comply with key financial standards. Leading ERP vendors offer vertical-specific versions of their software that incorporate business practices that are best for each sector.
An ERP is a critical business system that must mesh with how each company operates, so there is no one “best” platform. Required capabilities, preferred deployment model and company size will all affect your decision when buying an ERP system. Look to established vendors with proven records of success working with companies in your vertical. Always ask for reference customers, and check out success stories.
Businesses should also consider the software provider’s roadmap for emerging technologies like IoT and blockchain.
